RFID has developed several years and more and more mature in many kinds of applications , it is kinds of wireless data communication technology which it no needs to conntct power and passive working model . We can calssify different frequency and optional rfid chip according to which purpose we will use them .As one of leader rfid manufacturer China , Shenzhen ZhiJie IOT Application Co.,Ltd has invested advanced manufacturing equipment and researched different rfid products in different rough environment for meeting now many raising rfid solutions . Our rfid products whatever 125khz ,13.56mhz and 860-960mhz all are provided for our worldwide customers and got good reputation after they finished testing . Especially our unique antenna designs rfid sticker label in medical industry and work out many issues than our traditional barcode technology .
Numerous healthcare facilities have been deploying HF RFID technology to address patient safety, medication tracking and equipment hygiene issues to ensure a safe environment for patient care.
To meet this need, technology company ELATEC is providing such solutions to help healthcare organizations identify healthcare workers, patients, drugs and assets. The company says its goal is to ensure the proper handling and distribution of products, devices or patient services, and to protect access to patient electronic records.
Solutions being used by ELATEC's customers and solution providers include RFID-enabled ward carts to identify healthcare workers and secure patient bed affairs. In addition, the company supports multimedia terminals in each ward that utilize RFID readers to identify patients or healthcare workers, as well as the identification of authorized parties for RFID-based hospital ultraviolet (UV) disinfection systems.
At the heart of these solutions are ELATEC's TWN4 series of passive 13.56 MHz HF RFID readers that comply with the ISO 15693 standard.
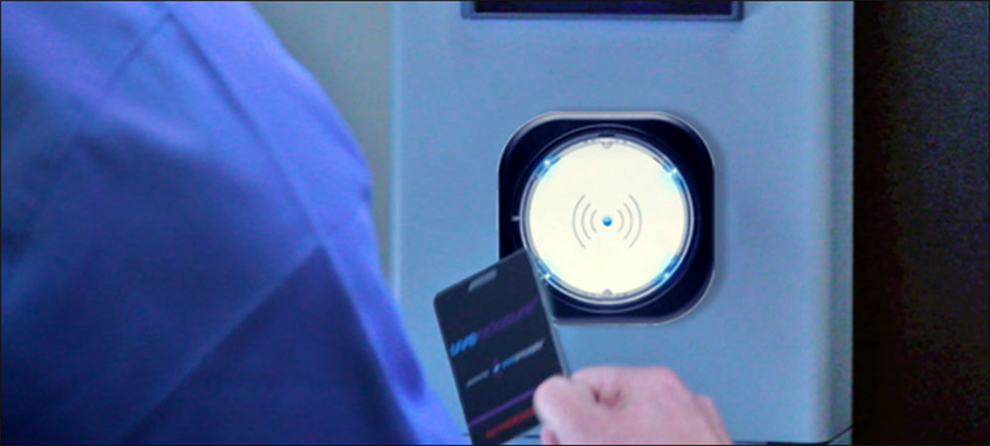

In January 2020, the UV-Concepts system was launched, which complements the cleaning and disinfection process of equipment in hospitals or other medical institutions. These devices incorporate an ELATEC reader to authenticate the identity of each user using the sterilized device. Each tag read creates a digital record of the event.
According to U-Concepts co-founder and CEO Jeremy Starkweather, UV-Concepts offers an enclosed UV radiation device called a UV Envelope (UVE) that is currently being used in academic and community hospitals and U.S. government-run medical centers.
Since its inception, U-Concepts has installed UV-Concepts systems at around 20 sites.
"Using our technology is a significant improvement over standard operating procedures for cleaning and sterilizing equipment in healthcare settings," Starkweather said. Ultraviolet light is effective at killing microbes within UVE units, but the system requires the personnel who use the equipment. To be authorized and clearly identified. Therefore, UVE has a built-in RFID badge reader.
Before use, healthcare workers first bring items such as wheelchairs to UVE for disinfection. They start by placing the HF RFID badge associated with their identity, lightly near the reader. If they are authorized to use the device, the device will unlock and allow the wheelchair to enter.
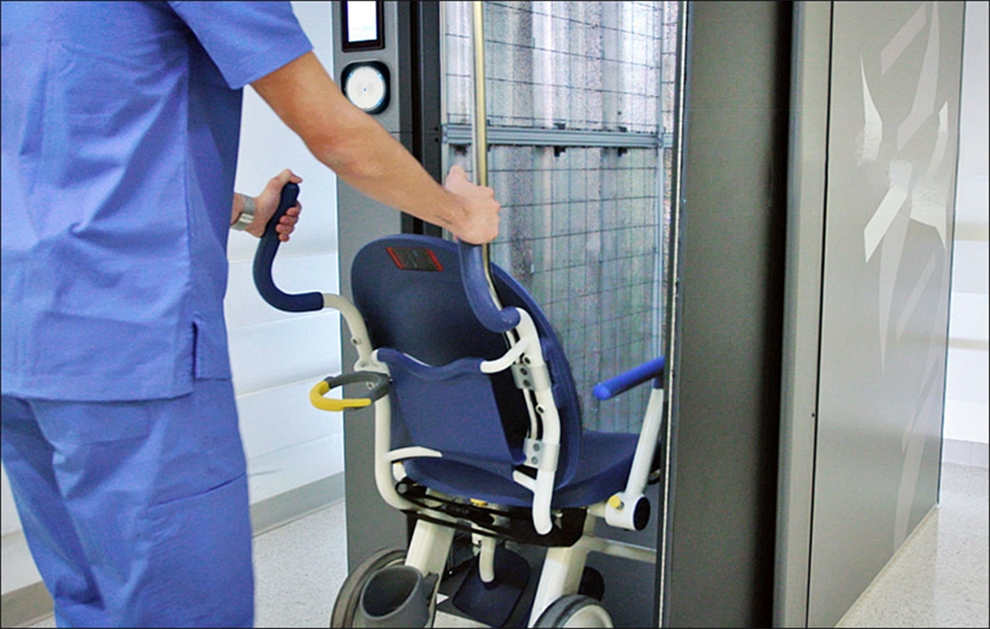
Healthcare workers must use the same badge again to close the door and turn on the disinfection system, initiating a six-second cycle. This ensures that the process has been completed by a trained user. If the individual is not authorized to use the device, the device will not function. The UVE system can also access devices using Bluetooth tags, which are recognized by beacons inside the device. Therefore, cloud management software can know who has used the device through RFID data, or which devices have been sterilized through Bluetooth transmission.
Sean Houchin, ELATEC's product manager, said ELATEC has been providing other solution providers with systems to protect patient data. For example, RFID badges carried by healthcare workers can uniquely identify healthcare workers as they provide patient care. Sometimes, staff use ward carts to deliver medicines, which are equipped with RFID readers. Hospitals use small handheld barcode scanners. When treating patients at the bedside, staff can read the HF RFID badge to identify themselves and then scan the patient's wristband. If anesthesia is used during treatment, the cart can remain locked until both the patient and medical staff are identified.
Once authorized, employees can use the medication in the cart. By reading the tags on the patient's wristband, hospital staff can clearly identify the patient they are caring for as the person to whom they should dispense medication. The software can display patient record information, and healthcare workers can ensure that the medication they are dispensing matches what is prescribed. The software can display information about appropriate dose levels, and the data collected can be used to manage inventory and trigger billing, Huchin said.
In addition, the system manages patient records, including printed materials, to ensure hospitals are in compliance with the HIPAA Act. If doctors, nurses or administrators need to provide paper documents to patients, they can use ELATEC's technology, which integrates HF readers into printers, to identify individuals before releasing documents to be printed. The document does not start printing until the person presents the RFID employee ID card (or mobile-authenticated smartphone) within the range of the integrated reader. This way, hospitals can ensure that only authorized individuals have access to documents.
ELATEC's technology is also used in the laboratory to track patient samples to ensure they are not mishandled or lost. In such a case, an RFID tag would be attached to the sample or vial. When the sample is put into a diagnostic machine, an RFID reader attached to the device reads the tag, authenticates the sample and displays the necessary information. Data captured from the event can be stored in the hospital's software to confirm which diagnostic tests were performed when and by whom.
"Tracking laboratory samples has become a very big need," Huchin said.
ELATEC readers support multimedia terminals that patients can use to access entertainment services during their hospital stay. Bedside touchscreen terminals allow patients to place orders from cafeterias or vending machines, as well as access TV or Internet services. Both patients and medical workers can first identify themselves with an RFID badge or wristband in order to gain access to the terminal. In addition, physicians can obtain digital information from the patient's bedside.
Ultraviolet sanitation technology can reduce the risk of transmission of health-associated infections (HAIs) through contaminated surfaces and is of increasing concern to healthcare organizations. Starkweather believes that relying on manual cleaning and disinfection processes alone cannot address this risk, and medical equipment can become contaminated with deadly pathogens, at rates as high as 30 to 50 percent in many hospitals. With contamination rates so high, healthcare organizations have been approaching technology companies in hopes of adding a layer of effectiveness.
Statement : Pictures above only show the product ,the intellectual property rights of the logo owned by their trademark .

